El Nino Explained: Future Challenges for the Himalayas & Beyond
Indian Himalayas
The Indian Himalayas, with their unique geography and diverse ecosystems, have long been subjected to the influences of El Nino events, and climate change. This research piece aims to provide a comprehensive historical analysis of the interactions between these phenomena and their impacts on the region.
By examining dated references and factual history, we explore the relationships between El Niño events, and climate change in the Indian Himalayas, shedding light on their implications for the environment, society, and the future of this fragile region.
El Nino:
The El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a climate pattern that occurs every few years in the tropical Pacific Ocean. During an El Niño event, the trade winds weaken, causing warm water to build up in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean. This warm water then spreads east, affecting weather patterns around the world.
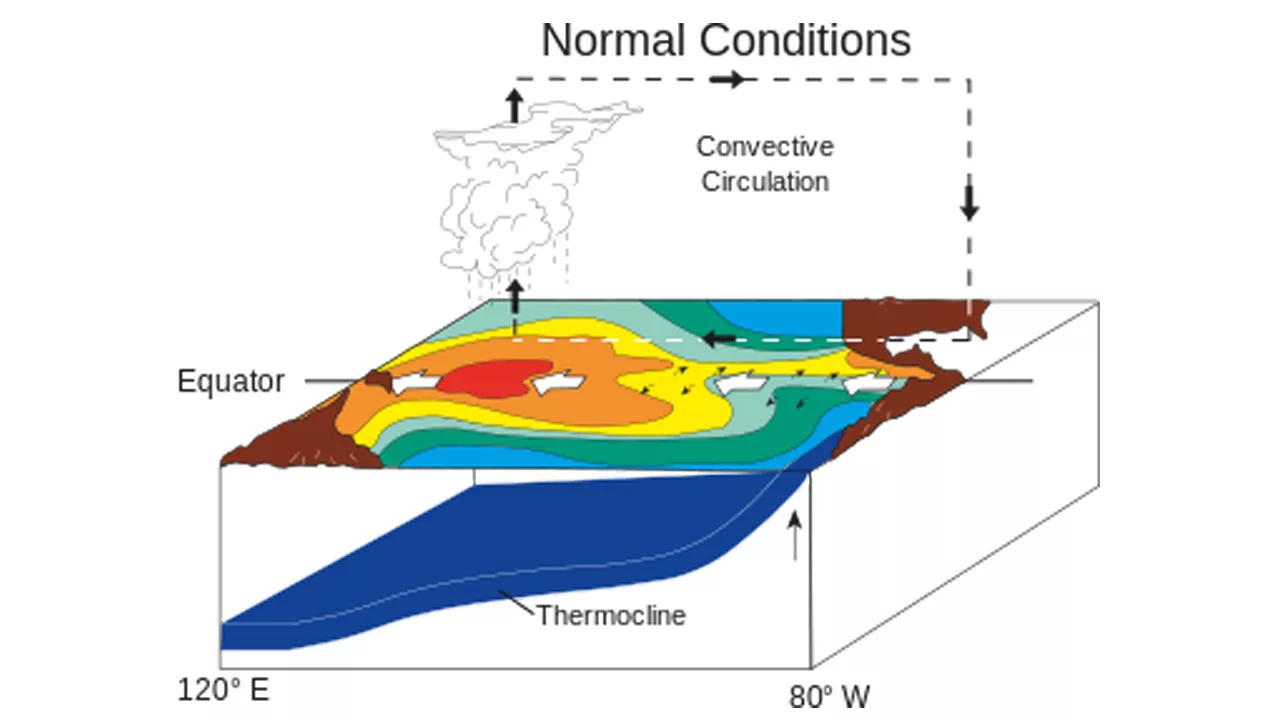
ELI5 – Explain Like I’m 5: El Nino
Imagine you’re at a beach and you notice that the water is usually warm and pleasant to swim in. But sometimes, things change, and the water becomes colder, and the waves get bigger. That’s kind of what El Niño is like but in a much bigger way.
Typically, the Pacific Ocean’s ocean water near the equator is colder in the east and warmer in the west. But sometimes, every few years, something happens that changes this pattern. When that happens, it’s called El Niño.
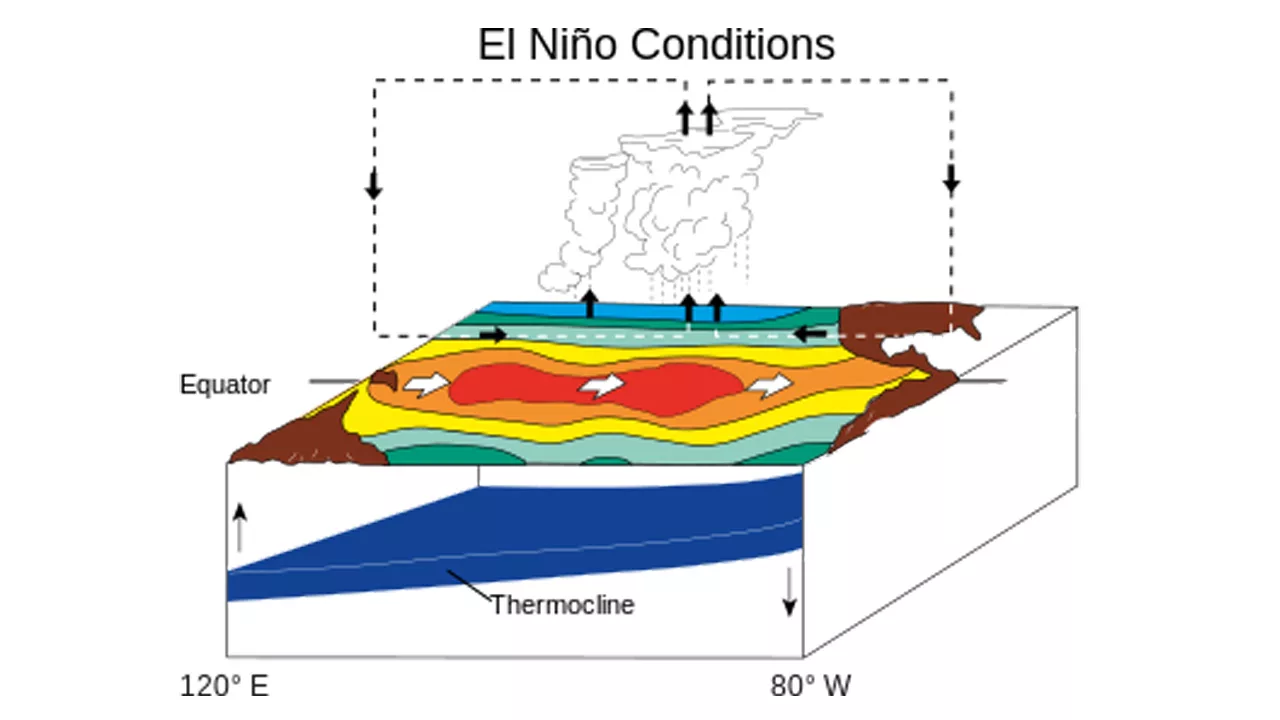
- During El Niño, the warm water that is usually in the west starts moving eastward, towards the coast of South America. As a result, the water in such locations becomes warmer than typical. And because the ocean and the atmosphere are connected, it also affects the weather.
- When El Nino happens, it can produce significant shifts in weather patterns throughout the planet. Some places might get more rain than usual, while others might get less rain and become drier. It can also make certain areas hotter than usual.
So, El Nino is a major shift in the water and weather that occurs every few years. It can make some areas wetter and others drier, and it affects the temperature of the water and the air.

El Niño and the Himalayas: Impacts and Adaptation
The Himalayas are a mountain range that stretches across Asia, forming a natural barrier between the Indian subcontinent and the Tibetan Plateau. The Himalayas support a diverse variety of ecosystems, including forests, glaciers, and snow-capped summits. The region is also home to millions of people who depend on the mountains for their livelihoods.
Less rainfall and snowfall in the Himalayas
One of the most significant impacts of El Nino on the Himalayas is a decrease in precipitation. This is due to the weakened trade winds during El Nino events allowing warm, dry air to flow from the north into the region. This can lead to drought conditions, which can damage crops and water supplies.
El Niño events can have a significant impact on the Himalayas. During an El Niño event, the Himalayas typically receive less rainfall and snowfall. This can lead to droughts, water shortages, and crop failures.

Heat waves and extreme weather in the Himalayas
El Niño events can also cause an increase in temperature. This is because the warm water in the Pacific Ocean during El Niño events can cause the atmosphere over the Himalayas to warm. This can lead to heat waves and other extreme weather events.
Increased snowfall and glacier growth in the Himalayas
The impacts of El Niño on the Himalayas are not always negative. In various circumstances, El Niño events can lead to increased snowfall and glacier growth. However, the overall impact of El Niño on the Himalayas is negative. El Niño events can also increase the risk of landslides and floods.

Climate Change
The impacts of El Niño on the Himalayas are likely to become more severe in the future due to climate change. Climate change is causing the Earth’s atmosphere to warm, which is leading to more extreme weather events. This means that the Himalayas are likely to experience more frequent and severe droughts, floods, and landslides in the future.
Here are some of the potential implications of El Niño for the Himalayas:
- Increased risk of drought and water shortages
- Increased risk of heat waves and other extreme weather events
- Reduced snow cover and glacier melt
- Increased risk of landslides and avalanches
- Damage to crops and ecosystems

Several options are available to adapt to the impacts of El Nino on the Himalayas. These include:
- Building dams and reservoirs to store water during wet years
- Developing drought-resistant crops – Examples: Pomegranate, Beans, Carrots, Corn instead of Squash, Watermelons, Peppers
- Improving early warning systems for floods and landslides
- Educating people about the risks of El Niño

The Himalayas are a vital part of the global climate system. The impacts of El Niño on the Himalayas can have a significant impact on people and ecosystems around the world. It is important to take steps to adapt to the impacts of El Niño to protect the Himalayas and the people who depend on them.
Historical Background El Nino events:
Early Observations:
The earliest documented references to anomalous weather patterns in the Indian subcontinent can be traced back to ancient texts, including the Vedas and the Mahabharata. These ancient records mention irregularities in monsoon rainfall, which could potentially be associated with El Niño events.
European Colonial Period:
During the European colonial era, British meteorologists established weather stations across India, contributing to the systematic collection of climate data. Historical records from this period provide evidence of El Niño events, linking them to below-average monsoon rainfall and associated societal impacts in the Indian Himalayas.
El Nino Events and Impacts in the Indian Himalayas:
Historical Data:
By analyzing historical meteorological records and paleoclimatic reconstructions, scientists have identified several El Niño events that influenced the Indian Himalayas. Notable events include the El Niño of 1877, which caused severe droughts and crop failures in the region, resulting in widespread socio-economic consequences.

Implications for Glacial Retreat:
Climate change-induced warming exacerbates the impact of El Niño events in the Indian Himalayas, particularly on glaciers. Historical data shows a correlation between El Niño events and accelerated glacial retreat. Increased meltwater from glaciers poses significant challenges for downstream communities, affecting water availability, agriculture, and hydropower generation.
El Nino and Ecological Consequences:
El Niño events and climate change have far-reaching ecological implications in the Indian Himalayas. Changes in precipitation patterns, increased temperatures, and altered ecosystems affect biodiversity, vegetation distribution, and wildlife habitats. This can disrupt delicate ecological balances and lead to the loss of endemic species.

El Nino and Mountaineering
El Niño events also have significant implications for mountaineering activities in the Indian Himalayas. The changing weather patterns associated with El Niño, such as altered precipitation and increased temperatures, can directly impact the safety and feasibility of climbing expeditions. Warmer temperatures can lead to increased snowmelt, which in turn can contribute to unstable conditions, avalanches, and glacial hazards. Additionally, irregular or reduced monsoon rainfall during El Niño years can affect the availability of water sources and pose logistical challenges for climbers.
Mountaineering communities and expedition planners must take into account the historical patterns of El Niño events while assessing risks and making informed decisions to ensure the safety of climbers in the Indian Himalayas. Continued monitoring and research on the relationship between El Niño and mountaineering will be crucial for developing effective strategies and guidelines in the face of climate change.
Historical Statistics on El Niño and the Himalayas:
1982-83 El Nino
- The 1982-83 El Niño event was one of the strongest on record.
- It caused widespread droughts in the Americas, Australia, and Africa.
- In the Himalayas, the event led to a decrease in rainfall and snowfall, which caused water shortages and crop failures.
- The event also increased the risk of landslides and floods.
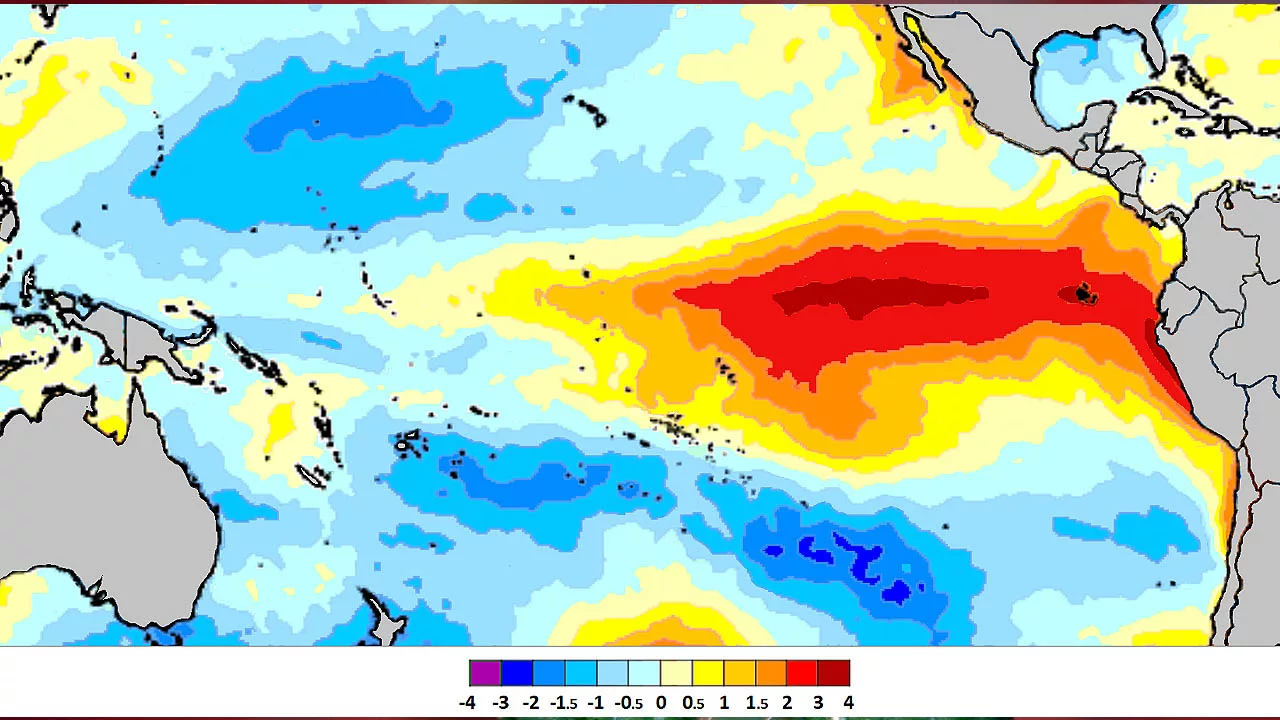
1997-98 El Nino
- The 1997-98 El Niño event was also one of the strongest on record.
- It caused widespread droughts and floods around the world.
- In the Himalayas, the event led to a decrease in rainfall and snowfall, which caused water shortages and crop failures.
- The event also increased the risk of landslides and floods.
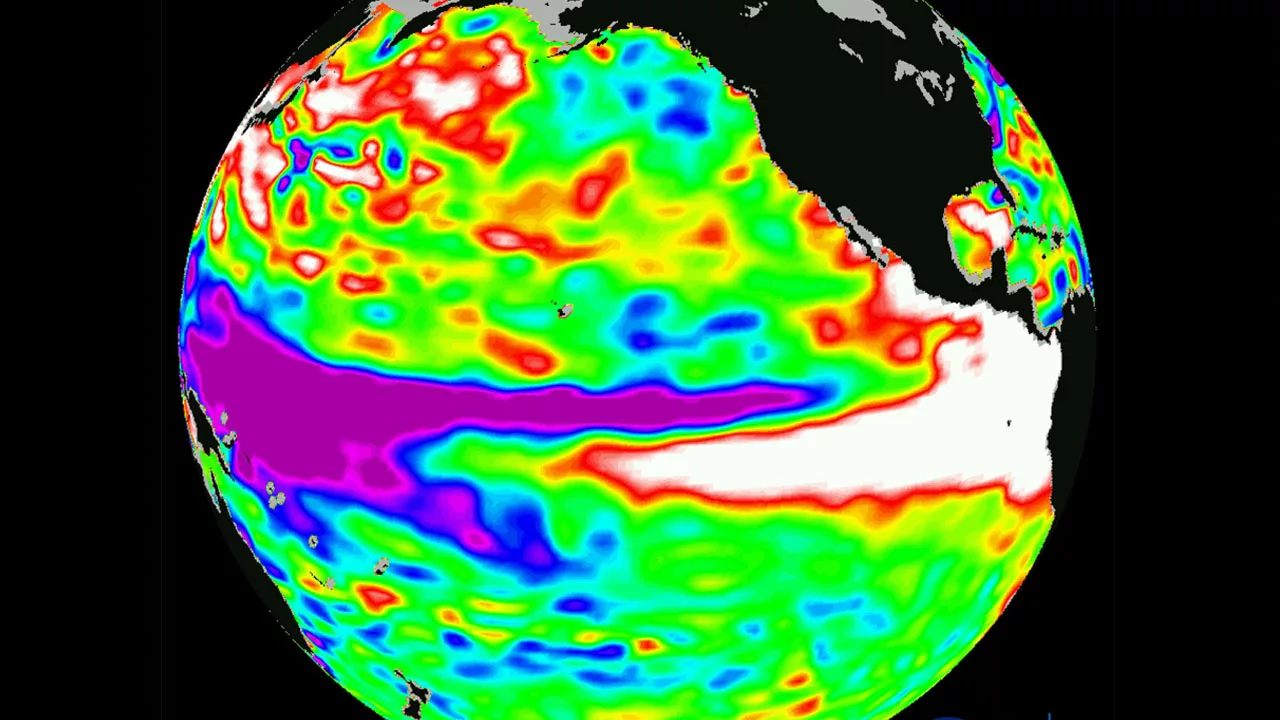
2015-16 El Nino
- The 2015-16 El Niño event was the strongest on record since 1997-98.
- It caused widespread droughts and floods around the world.
- In the Himalayas, the event led to a decrease in rainfall and snowfall, which caused water shortages and crop failures.
- The event also increased the risk of landslides and floods.
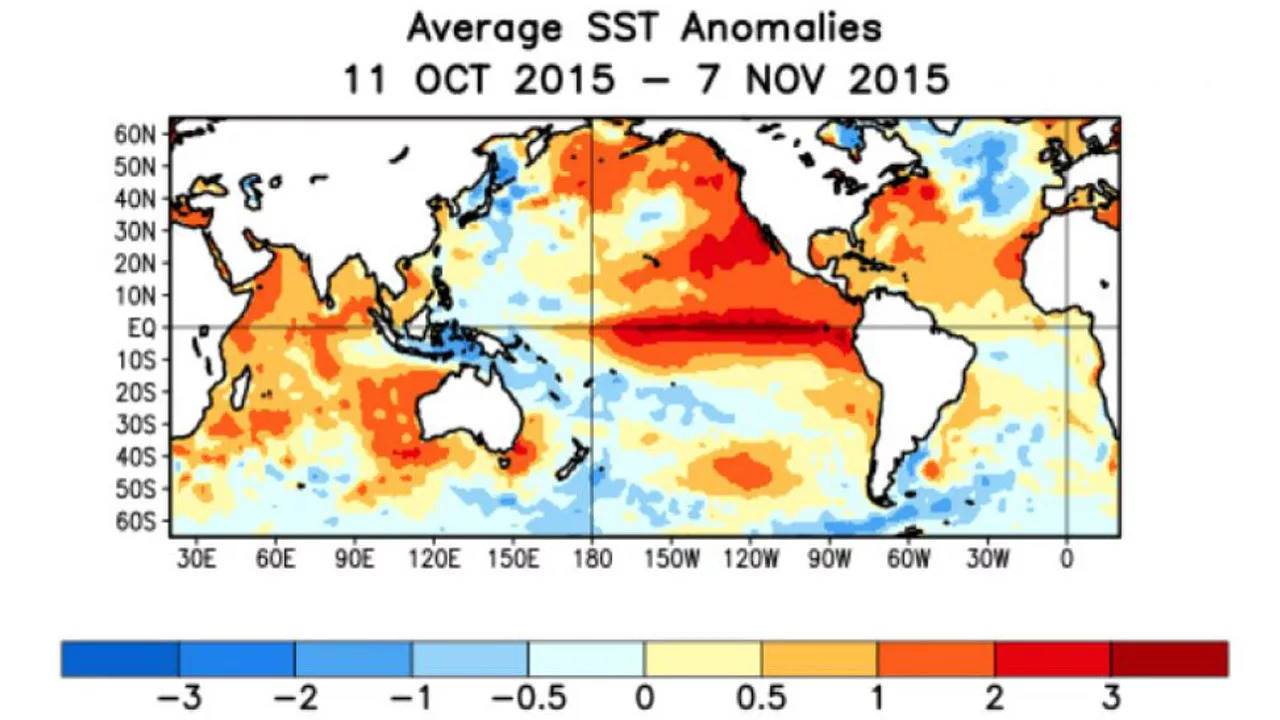
These are just a few examples of the historical impacts of El Niño on the Himalayas. The impacts of El Niño are likely to become more severe in the future due to climate change. It is important to take steps to adapt to the impacts of El Niño to protect the Himalayas and the people who depend on them.
La Niña
La Niña is the opposite of El Niño. Remember how we talked about El Niño making the ocean water warmer and changing the weather? Well, La Niña does something similar, but in the opposite direction.
During La Niña, the ocean water in the eastern Pacific Ocean near the equator becomes even colder than usual. It’s like the ocean is getting a little extra icy. This colder water affects the weather patterns too.
When La Niña happens, it can make some places colder and drier. So, imagine if you’re used to wearing a light jacket outside, but during La Niña, you might need a warmer jacket because it gets even chillier. It can also cause less rain in some areas, which means those places might become drier than usual.
Just like El Niño, La Niña affects the whole world’s weather. It can change how much rain some places get, make some areas colder, and even affect storms and hurricanes. So, while El Niño is like a warm change, La Niña is like a cool change in the ocean and the weather.
2023 – El Nino
There is a 60% chance for a transition from ENSO-neutral to El Niño during May-July 2023, and this will increase to about 70% in June-August and 80% between July and September, according to the Update, which is based on input from WMO Global Producing Centres of Long-Range Forecasts and expert assessment.
At this stage there is no indication of the strength or duration of El Niño
Geneva, 3 May 2023 – World Meteorological Organization (WMO)
Future Outlook:
As the global climate continues to change, it is crucial to understand the potential future scenarios for El Niño events and their impacts on the Indian Himalayas. Climate models project an increase in the frequency and intensity of El Niño events due to global warming, which could have severe consequences for the region’s vulnerable ecosystems, communities, and water resources.

Conclusion:
The historical perspective on El Niño events and climate change in the Indian Himalayas provides valuable insights into the interactions between natural climate variability and anthropogenic influences. By understanding the historical occurrences and consequences, we can enhance our preparedness for future climatic challenges. It is imperative to prioritize climate change mitigation and adaptation measures to safeguard the fragile ecosystems and communities of the Indian Himalayas.
Related Readings:
Nature’s Clues: A Guide to Weather Signs in the Great Outdoors
References
- Diaz, H. F., & Markgraf, V. (Eds.). (2000). El Niño and the Southern Oscillation: Multiscale variability and global impacts. Cambridge University Press.
- Shukla, J., & Paolino, D. A. (1983). The Southern Oscillation and long-range forecasting of the summer monsoon rainfall over India. Monthly Weather Review, 111(9), 1830-1837
- Y DING (2004). Inter decadal variability of the Asian summer monsoon and its relation to global climate change. Climate Dynamics, 23(2-3), 257-276.
- Gadgil, S., & Gadgil, S. (2006). On the Climate of South Asia. Journal of the Indian Institute of Science, 86(5), 489-502.
- Philippus Wester, Arabinda Mishra, Aditi Mukherji, Arun Bhakta Shrestha, (2019). The Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment: Mountains, Climate Change, People. Kathmandu: ICIMOD.
- Immerzeel, W. W., Aditi. (2019). The water towers of Asia: A review of trends in snow, glacier and water resources in the Hindu Kush Himalaya region. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 64(1), 1-22.