Super El Niño Unleashed: 2024 Spring Holds Historic Potential
Blogs
This weather event has a 1 in 3 probability of becoming a “historically strong” Super El Niño, causing global temperatures to rise even further. Meteorologists and climate experts are concerned and interested since there is a 54% chance that this event will be historically strong.
In a recent update from the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), the provisional State of the Global Climate report has confirmed that 2023 is on track to become the warmest year on record. The data, compiled until the end of October, reveals that the global temperature was approximately 1.40 degrees Celsius above the pre-industrial baseline of 1850-1900. This margin of warmth, with a small uncertainty of ±0.12°C, puts 2023 ahead of the previously record-setting years, 2016 and 2020.
Record-Breaking Warmth: WMO Confirms 2023 Trends
The emergence of a significant El Niño event during the Northern Hemisphere spring of 2023 is attributed to this unprecedented warmth. Although the WMO’s May report indicated a likelihood of El Niño, the strength, and duration were uncertain at that time. El Niño typically peaks in its warming effect after emerging, and meteorologists now anticipate that this rapid development during the summer of 2023 will continue to influence global temperatures into 2024.
Regional Insights: Met Office’s Forecast for Himachal Pradesh
The Met Office has issued forecasts for Himachal Pradesh, indicating above-normal maximum and minimum temperatures over the next two months. Additionally, most parts of the country can expect above-normal minimum temperatures, excluding some areas in Northeast India where temperatures are expected to remain within the normal range.
Learn more about El Nino:

Looking Ahead: NOAA’s Predictions for Spring 2024
Looking ahead, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) predicts a “strong” Northern Hemisphere spring from March to May 2024. There is a notable 1 in 3 chance that this weather event could escalate to a “historically strong” Super El Niño, further intensifying the impact on global temperatures.
What is Super El Niño?
A “Super El Niño” refers to a powerful El Niño event, which is a climate phenomenon characterized by the periodic warming of sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean. El Niño events have widespread impacts on weather patterns across the globe.
During a Super El Niño, the warming of sea surface temperatures is particularly intense and can have more profound and far-reaching effects compared to regular El Niño events. These impacts may include:
1. Global Temperature Anomalies:
Super El Niño events are associated with higher-than-average global temperatures. The increased warming of the Pacific Ocean during such events can contribute to a significant rise in overall global temperatures.
2. Extreme Weather Events:
Super El Niño can lead to more intense and widespread weather extremes, including heavy rainfall, floods, droughts, and storms. The altered atmospheric circulation patterns associated with a Super El Niño can influence weather systems across different regions.
3. Shifts in Precipitation Patterns:
The warming of the central and eastern Pacific Ocean can influence the movement of the jet stream, leading to shifts in precipitation patterns. Some areas may experience increased rainfall, while others may face drought conditions.
4. Impact on Agriculture:
Changes in precipitation and temperature patterns can affect agricultural productivity. Regions may experience crop failures, changes in growing seasons, and disruptions to ecosystems.
5. Adventure Activities in the Himalayas Amidst Super El Niño:
The impending threat of a historically strong Super El Niño in 2023 poses significant challenges to adventure activities in the Indian Himalayas. The region, known for its awe-inspiring climbing, and treks, may experience unprecedented shifts in weather patterns and conditions. The elevated temperatures and potential alterations in precipitation associated with a Super El Niño can lead to unpredictable and potentially hazardous situations for mountaineers and trekkers. As the Himalayan landscape is particularly sensitive to climate variations, the usual routes and conditions for adventure activities may be affected. Adventure travel companies like Ascent Descent Adventures need to closely monitor developments, reevaluate safety protocols, and adapt itineraries to ensure the well-being of participants. This underscores the importance of staying informed about climate patterns and embracing flexibility in planning to navigate the challenges presented by a changing climate, especially in the context of extreme events like a Super El Niño.
It’s important to note that not every El Niño event develops into a Super El Niño. The strength and intensity of El Niño events can vary, and meteorological organizations closely monitor and forecast these events to provide early warnings and help communities prepare for potential impacts. The term “Super El Niño” is used to describe the most powerful and rare instances of this climate phenomenon.
Current El Niño Status:
El Niño is currently active and rapidly progressing in the tropical Pacific, contributing to shifts in global weather patterns. The 54% probability of this event becoming historically strong raises concerns and interest among meteorologists and climate scientists.
Implications of a Historically Strong or Super El Niño:
A historically strong El Niño can have profound impacts on weather systems worldwide. The consequences can be significant and diverse from altering precipitation patterns to influencing temperatures. It’s essential for various sectors, including agriculture, water resource management, and disaster preparedness, to stay informed and adapt to potential changes.
Transition to ENSO-Neutral:
Despite the current strength of El Niño, forecasts indicate a transition to ENSO-neutral conditions by April to June 2024. This shift is expected to have important implications for climate patterns, as the tropical Pacific settles into a more neutral state.

Why the Transition Matters:
The transition from El Niño to ENSO-neutral conditions marks a crucial period. Understanding and preparing for these shifts is vital for industries and communities that rely on predictable weather patterns. ENSO-neutral conditions provide an opportunity for a more stable climate outlook, albeit with its unique set of challenges.
Looking Ahead:
As we approach the coming months, monitoring the evolution of El Niño and the subsequent transition to ENSO-neutral conditions becomes paramount. This information is crucial for making informed decisions in various sectors, ranging from agriculture and energy to disaster management.
Conclusion:
As climate patterns continue to evolve, the data underscores the importance of monitoring. And understanding the complex interplay between El Niño events and global climate conditions. These findings provide valuable insights for individuals, communities, and policymakers as they navigate the challenges of a changing climate. Stay tuned for further updates as scientists and meteorologists closely observe and analyze these dynamic weather patterns.
Rising Thermometers: El Niño 2024 Unveiled
Unveiling the Dynamics of El Niño 2024: Insights from Scientific Reports
The year 2023 marked the inception of a climatic narrative poised to shape global temperatures on an unprecedented scale. In a recent study published in the journal Scientific Reports, researchers have unveiled compelling insights into the looming El Niño event of 2024 and its profound implications for our planet’s climate dynamics.
El Niño, the notorious disruptor of atmospheric tranquility, emerges as the harbinger of a global upsurge in surface air temperatures (SAT). With an estimated 90% likelihood of surpassing historical records, the impending warmth casts a looming shadow over regions far and wide, heralding a new era of climate extremes.
Drawing on meticulous analysis, the study illuminates the intricate dance between El Niño and the persistence of climate signals, underscoring their formidable influence on regional SAT variability. From the bustling coasts of Asia’s Bay of Bengal to the tranquil depths of Alaska and the Amazon basin, no corner of the globe remains untouched by the specter of rising temperatures.
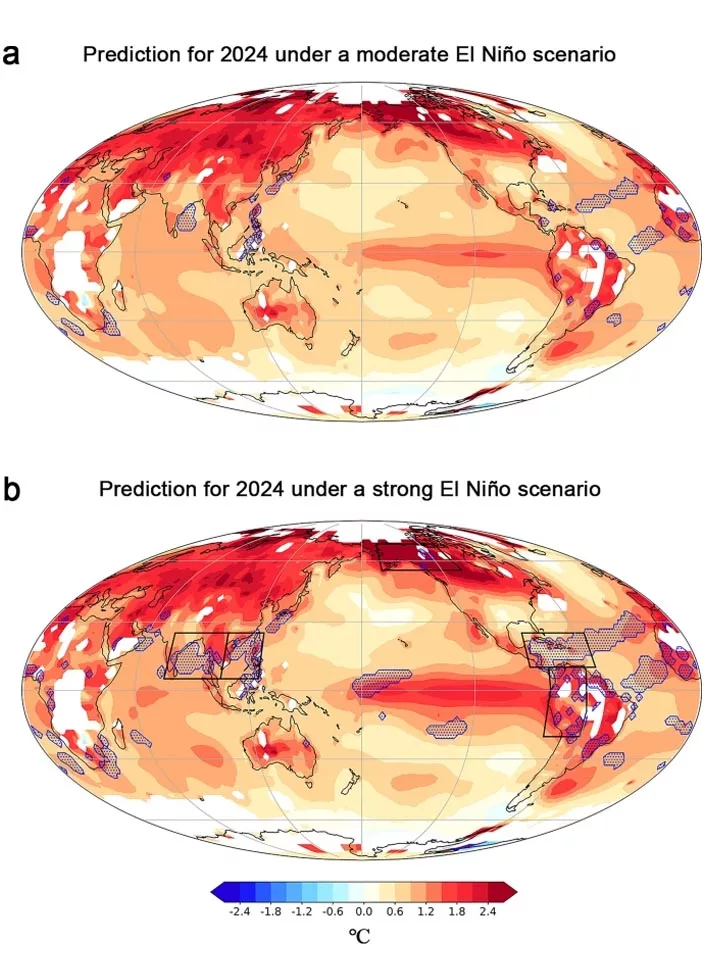
Unraveling the Climate Tapestry: The Influence of El Niño on Global Surface Temperatures
The heartbeat of El Niño lies in the vast expanses of the eastern equatorial Pacific, where sea surface temperature anomalies serve as harbingers of climatic upheaval. As the ocean relinquishes its heat to the atmosphere, atmospheric heating accelerates, propelling global surface temperatures to unprecedented heights.
However, the ramifications extend beyond mere thermometric readings. The study unveils a tapestry of ecological, economic, and social consequences, woven by the tendrils of record-breaking warmth. Year-round marine heatwaves loom ominously over the Bay of Bengal, the South China Sea, and the Caribbean, portending upheaval in ecosystems and livelihoods alike.
Charting the Course: Navigating the Nexus of Climate Variability and Mitigation
Yet, amidst the cacophony of climatic uncertainty, hope flickers in the corridors of understanding. The study elucidates the delicate interplay between El Niño and greenhouse gas forcing, illuminating pathways for strategic mitigation measures. From rapid rises in global mean surface temperature (GMST) during El Niño’s reign to the tempered lulls of La Niña’s embrace, the pendulum of climate variability swings with a rhythmic cadence.
In the wake of these revelations, the urgency of proactive measures emerges as a clarion call. Strategic mitigation efforts, tailored to the nuances of regional vulnerability, offer a beacon of hope amidst the gathering storm. From the corridors of policy to the trenches of grassroots activism, a united front against climate adversity beckons.
As we stand on the cusp of climatic uncertainty, the lessons of El Niño 2024 echo with resounding clarity. In the crucible of adversity, humanity finds its mettle tested. Let us rise to the occasion, forging a path toward a future where the tempests of uncertainty yield to the promise of resilience and renewal.
Related Readings:
Nature’s Clues: A Guide to Weather Signs in the Great Outdoors