Mountaineering and Alpinism: Conquer or Explore
Indian Himalayas
Introduction: Differences Between Mountaineering and Alpinism
Mountaineering and Alpinism are two different mountain exploration and climbing disciplines. While they have certain commonalities, they also have significant variances. This article aims to deliver a detailed review of the qualities of mountaineering and Alpinism, stressing their distinct features and evaluating the specific abilities and objectives connected with each activity.
Definition and Scope:
a. Mountaineering: Exploring the Wide Spectrum of Mountain Climbing
A broad term encompassing various activities related to climbing mountains, often involving treacherous terrains, glaciers, and technical rock faces.
b. Alpinism: Unleashing the Adventure in High-Altitude and Technical Climbing
A subset of mountaineering that focuses on climbing in high-altitude and technically challenging environments characterized by extreme weather conditions, steep ice slopes, and dangerous rock formations.
Objectives
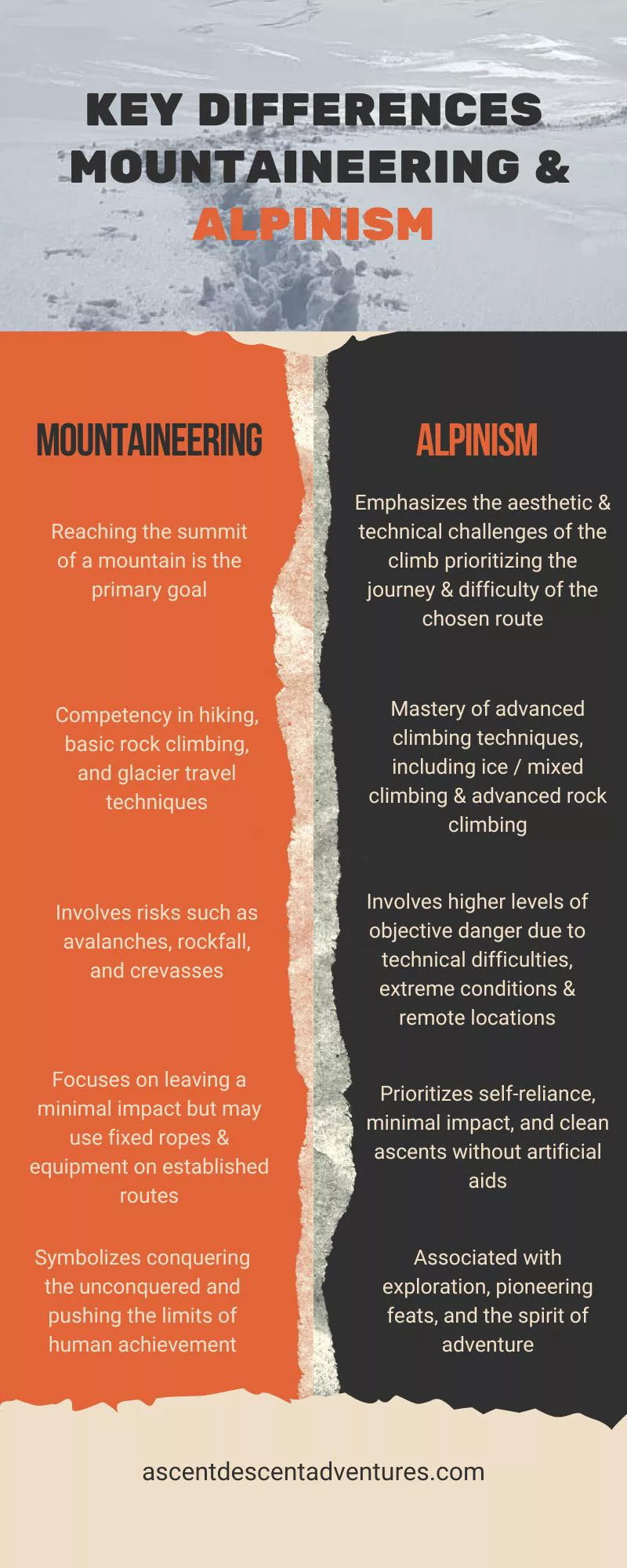
a. Mountaineering: Scaling Summits and Embracing Natural Beauty
Primarily focuses on reaching the summit of a mountain as the goal, with an appreciation for the surrounding natural beauty and personal growth.
b. Alpinism: The Pursuit of Aesthetics and Technical Challenges
Emphasizes the aesthetic and technical challenges of the climb, prioritizing the journey and difficulty of the chosen route, often exploring new or rarely climbed lines.

Technical Skills
a. Mountaineering: Essential Skills for Mountain Conquerors
Requires competency in hiking, basic rock climbing, glacier travel techniques, navigation, weather pattern understanding, and equipment usage. In addition, a large crew of potters is usually there to transport equipment and supplies.
b. Alpinism: Mastering Advanced Techniques for Alpine Explorers
Demands mastery of advanced climbing techniques such as ice climbing, mixed climbing, and progressive rock climbing techniques. Route finding, assessing hazards, and decision-making in high-stress situations are essential skills. Alpinists must be self-sufficient, carrying their equipment and supplies for extended periods.

Risk and Ethical Considerations
a. Mountaineering: Navigating Risks and Upholding Ethics
Involves risks such as avalanches, rockfalls, and crevasses. Often takes place on established routes with access to rescue infrastructure and higher human activity, reducing certain risks.
b. Alpinism: Tackling Extreme Challenges with Care and Responsibility
Alpinism presents a higher degree of danger due to technical difficulties, extreme conditions, and remote locations. Alpinists face exposure to unpredictable weather, rockfall, unstable ice, and other hazards. Meticulous planning and heightened risk management are crucial. Ethical considerations promote minimal impact, self-reliance, and a clean ascent without artificial aids.

Cultural and Historical Significance
a. Mountaineering: A Historical Tapestry of Triumph and National Pride
It has a long history of capturing the imagination of explorers and adventurers, symbolizing the conquering of the unconquered and pushing the limits of human achievement.
b. Alpinism: Pioneering Feats and the Spirit of Adventure
Associated with pioneering feats, exploration, and the spirit of adventure. The golden age of Alpinism saw the exploration of iconic peaks in the Alps. Legendary personalities in the history of Alpinism pushed the boundaries of what was considered possible.

Bottomline: Mountaineering vs. Alpinism
Mountaineering and Alpinism, while sharing a common foundation in mountain climbing, differ in objectives, technical skills, risk considerations, and cultural significance. Mountaineering focuses on reaching summits, often following established routes, while Alpinism emphasizes exploration, technical difficulty, and self-reliance in challenging environments. Both disciplines offer unique experiences and challenges, attracting individuals with diverse motivations and aspirations in their mountain pursuits.
Ready to practice Alpinism? Check out our 7-day Alpine Training course
Learn More About Mountaineering vs Trekking

FAQ:
What Is the Difference Between Mountaineering, Hiking, and Trekking?
Mountaineering is the practice of climbing mountains and generally necessitates technical abilities, specialized equipment, and knowledge of rope methods, ice climbing, and other advanced mountaineering skills. Hiking, on the other hand, refers to walking on trails or routes in natural settings, often on lower-altitude terrain, and it usually does not need any specialized skills or equipment beyond essential hiking gear. In contrast, mountaineering is more difficult, hazardous, and more physically demanding than hiking.
Mountaineering involves climbing mountains, often technical and challenging, using specialized equipment and techniques, with a focus on reaching high-altitude summits. Trekking, on the other hand, refers to walking on established trails, usually in hilly or mountainous areas, without the need for technical climbing skills or equipment, often for recreational purposes or to explore natural landscapes.
Mountaineering is climbing mountains, which often necessitates technical abilities, specialized equipment, and previous training with ropes, harnesses, and other climbing techniques. Hiking is defined as walking on trails or walks in natural settings, typically on well-marked routes, with no substantial technical obstacles. Trekking is comparable to hiking in that it involves longer excursions, multi-day Himalayan trekking expeditions, and crossing distant or rough terrain, but it requires good stamina and logistical organization.
Alpine mountaineering is the activity of climbing mountains in Europe’s Alps mountain range. It entails climbing high slopes, negotiating glaciers, and dealing with a variety of problems, like harsh weather and technical issues. Alpine climbing necessitates a mix of physical fitness, technical abilities, and mountain knowledge. It is a difficult and thrilling quest that draws explorers and outdoor enthusiasts from all around the world.